In our world teeming with diverse forms of life, some of the most formidable adversaries we face are the ones invisible to the naked eye. Infectious diseases, caused by harmful microorganisms like viruses and bacteria, are a global health concern, prompting immense research and counteractive measures. This blog post will delve into the universe of infectious diseases, their impact, and the advances we’re making in battling these unseen foes.
Infectious Diseases: An Overview
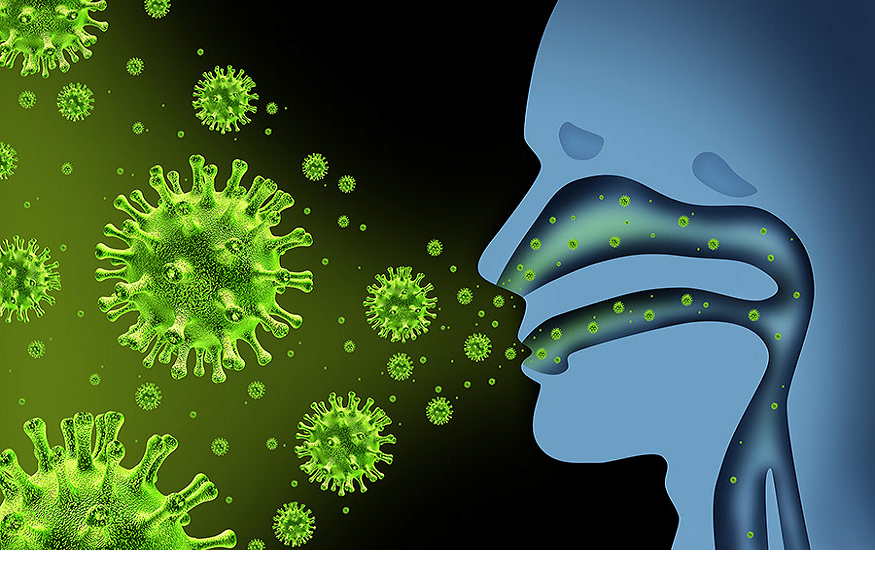
Infectious diseases are disorders caused by microorganisms, such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites. While many of these organisms exist harmlessly in our bodies or environment, others can invade our bodies and cause illness. Diseases can be transmitted in various ways, including direct contact, via insect or animal bites, or through contaminated water, food, or air.
The Villains: Viruses and Bacteria
Viruses: Viruses are tiny particles that invade host cells within our bodies and replicate. By hijacking our cells, they cause illnesses ranging from the common cold and flu to more serious diseases like HIV/AIDS and COVID-19.
Bacteria: Unlike viruses, bacteria are single-celled organisms that can survive independently. While many bacteria are beneficial, some can cause diseases such as tuberculosis, pneumonia, and foodborne illnesses.
Consequences of Infectious Diseases
Infectious diseases can have widespread impacts, from causing mild discomfort to sparking global pandemics. They account for a significant proportion of deaths worldwide, particularly in developing countries where access to healthcare can be limited. Moreover, the evolution of antibiotic-resistant bacteria presents a grave challenge, making some diseases harder to treat.
Combatting Infectious Diseases: Treatment and Prevention
Treatment of infectious diseases often involves antimicrobial medicines. Bacterial infections are typically treated with antibiotics, while antiviral drugs are used for viral infections. However, not all infections are treatable, and some viruses, such as those causing HIV/AIDS and certain forms of hepatitis, can only be managed, not cured.
Prevention is a crucial aspect of controlling infectious diseases. Hygiene practices, safe food preparation, immunisation, and safe handling of animals can prevent or reduce disease transmission. Vaccines have been paramount in preventing various infectious diseases, even eradicating some, like smallpox.
Research and Innovations: Hope on the Horizon
Research into infectious diseases is continually evolving. We’re learning more about how these diseases spread, how our bodies respond, and how best to treat them. One remarkable achievement has been the rapid development of vaccines for COVID-19, demonstrating the potential of global scientific collaboration.
Advancements in genomic sequencing have allowed researchers to track disease outbreaks and understand microbial resistance to drugs. Meanwhile, innovations in diagnostic technology enable faster, more accurate identification of infectious agents, leading to timely and effective treatment.
A Look Ahead
While we’ve made significant strides in understanding and controlling infectious diseases, the journey is far from over. The continued emergence of new pathogens and the challenge of antimicrobial resistance make it clear that this is an ongoing battle.
The future of infectious disease research and response will likely involve a combination of improved surveillance systems, rapid vaccine development, novel treatments, and public health interventions. Through continued research, innovation, and collaboration, we stand ready to confront the microbial threats that lie ahead.
In conclusion, infectious diseases have a significant impact on global health, but our growing understanding and evolving strategies bring hope. As we continue to explore the world of these microorganisms, our resilience and scientific progress shine as beacons guiding us towards a healthier future.