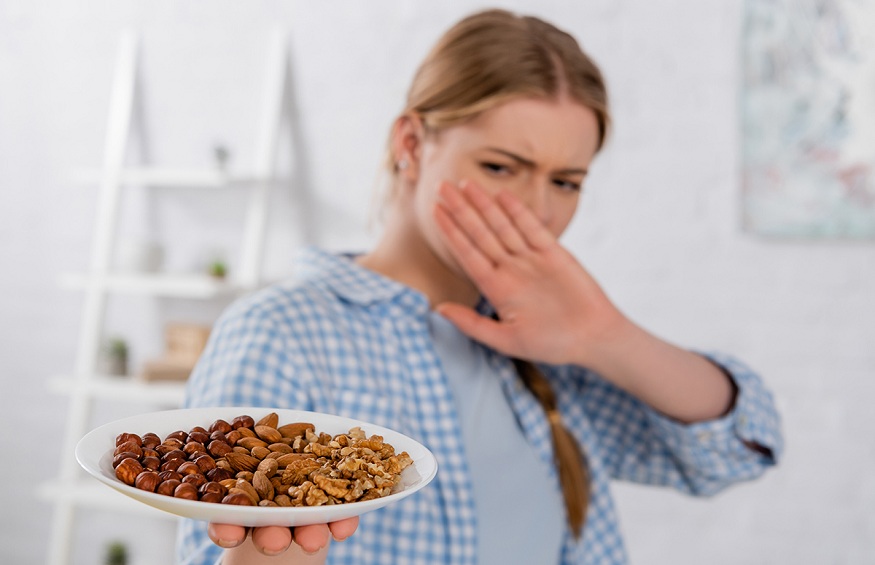
Living with a food allergy can present unique challenges in daily life, as it requires careful attention to the foods we consume and the environments we navigate. Food allergies occur when the immune system overreacts to specific proteins in food, leading to a range of symptoms, from mild discomfort to severe allergic reactions. While there is no cure for food allergies, effective management and treatment strategies can enable individuals to live healthy, fulfilling lives.
In this blog post, we will explore essential steps for managing food allergies and discuss available treatment options.
1. Accurate Diagnosis
The first step in managing a food allergy is obtaining an accurate diagnosis. If you suspect you have a food allergy, consult with an allergist or immunologist. They will conduct a thorough medical history review, possibly perform allergy testing (skin prick tests, blood tests, or oral food challenges), and interpret the results to identify the specific allergen(s) causing the allergic reaction.
2. Strict Avoidance
The cornerstone of managing a food allergy is strict avoidance of the allergen(s). This involves thoroughly reading food labels, being aware of cross-contamination risks, and understanding potential hidden sources of the allergen(s). It’s important to develop effective strategies for dining out, traveling, and communicating your food allergy needs to others, such as friends, family, and restaurant staff.
3. Emergency Preparedness
Despite precautions, accidental exposure to allergens can occur. It is essential to be prepared for allergic reactions by carrying an epinephrine auto-injector (such as an EpiPen) at all times, as prescribed by your healthcare provider. Ensure that family members, friends, and caregivers are trained in recognizing the signs of an allergic reaction and administering the auto-injector if needed. Promptly seek medical attention after using epinephrine.
4. Allergy Management Plan
Work with your allergist or immunologist to develop a comprehensive allergy management plan. This plan should outline specific steps to take in case of an allergic reaction, including emergency contact information, a list of allergens to avoid, and guidelines for when to seek medical attention. Regular follow-ups with your healthcare provider are crucial to update your management plan and address any concerns.
5. Education and Awareness
Education plays a vital role in managing food allergies. Stay informed about the latest research, resources, and guidelines related to your specific allergen(s). Educate yourself and others about the signs and symptoms of an allergic reaction, including anaphylaxis. Promote awareness in your community by advocating for allergy-friendly practices in schools, workplaces, and public spaces.
6. Ongoing Research and Treatment Options
Advancements in medical research are continually improving the understanding and treatment of food allergies. Here are some emerging treatment options:
– Oral Immunotherapy (OIT): OIT involves gradually exposing individuals to small, controlled amounts of the allergen(s) to desensitize the immune system. This therapy is currently being studied and shows promise for certain food allergies, but it should only be conducted under the guidance of an allergist or immunologist.
– Sublingual Immunotherapy (SLIT): SLIT involves placing small amounts of allergen extract under the tongue to induce desensitization. Like OIT, SLIT is still under investigation and should be done under medical supervision.
Living with a food allergy requires vigilance, preparation, and education. Strict avoidance of allergens, emergency preparedness, and clear communication are essential aspects of managing food allergies. Stay informed about the latest research and treatment options through regular consultations with healthcare providers and engagement with the food allergy community. With proper management and support, individuals with food allergies can lead healthy, fulfilling lives while minimizing the risk of allergic reactions.